Think your safest driver is the one you never hear about? Think again.
If you’re still relying on gut instinct or the absence of complaints to evaluate performance, you could be missing serious risk—or overlooking your top talent. The truth is, driver performance is the most critical factor in your fleet’s safety, efficiency, and reputation.
But without data, you’re left guessing.
According to the FMCSA, driver behavior contributes to over 85% of serious truck-related crashes. That’s not just a statistic—it’s a wake-up call.
Leading fleets are moving beyond outdated reviews and leaning into telematics, AI-powered dash cams, and real-time scorecards to make data-backed decisions. The result? Safer roads, smarter coaching, and more confident leadership.
This guide shows you how to stop guessing and start acting—with the tech that turns raw driving data into real-world performance wins.
The Real-World Cost of Driving Blind
You’ve got vehicles on the road, deliveries happening, and no complaints coming in. Everything seems fine—until it isn’t.
What you can’t see is what can hurt you the most. When fleets rely on opinions or incident reports instead of real-time data, dangerous driving behaviors, costly habits, and coaching gaps slip through unnoticed. It’s not just risky—it’s expensive.
Near-miss incidents often go undocumented because no tools were in place to catch them. Distracted driving and fatigue aren’t visible in a spreadsheet until they cause an accident. And when coaching isn’t backed by consistent data, it becomes subjective—leading to mixed messages and missed opportunities for improvement.
Worse yet, evaluation bias can creep in. Some drivers get the benefit of the doubt while others are unfairly flagged. That lack of transparency can damage morale and trust across your team.
Insurance providers notice too. Fleets that lack a data-driven safety program tend to face higher premiums and slower claims resolutions. Without proof, even minor incidents can spiral into major liability.
Industry Snapshot:
One national waste management fleet faced recurring pedestrian close calls from sudden hard braking. But without video evidence or performance data, they had no way to verify incidents, coach drivers, or defend against liability. Insurance rates climbed, while accountability slipped.
The takeaway? You can’t fix what you can’t see—and waiting for a major incident to act is simply too late.
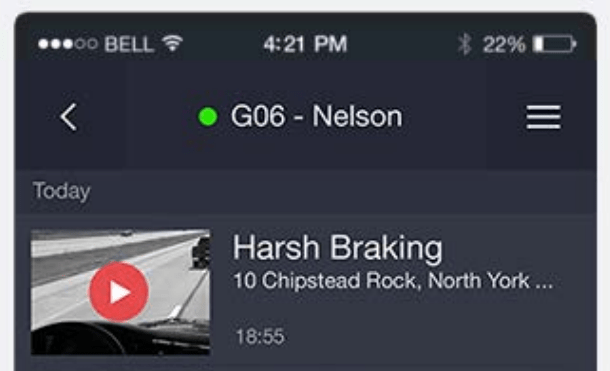
From Footage to Feedback: The Role of AI Dash Cams
If blind spots are the problem, visibility is the solution—and that’s where dash cams go from nice-to-have to non-negotiable.
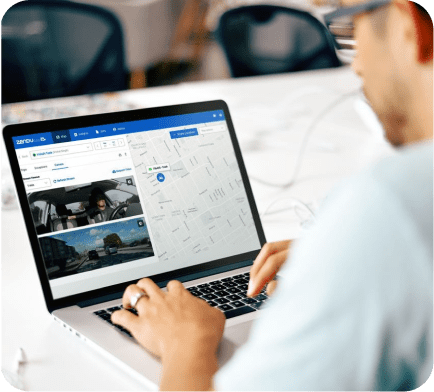
In the last section, we looked at what happens when you can’t see what your drivers are doing in real time. Now let’s talk about how to fix that. AI-powered dash cams give you a front-row seat to what’s happening behind the wheel—and more importantly, what to do about it.
These aren’t your standard recording devices. Modern dash cams are equipped with features like Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), motion detection, and fatigue monitoring. They don’t just record—they analyze. The second a driver shows signs of distraction or risky behavior, the system delivers a real-time alert, giving them a chance to course-correct on the spot.
Even better, fleet managers get instant access to event footage, whether it’s for internal coaching or resolving an insurance claim. If there’s ever a dispute, dash cams provide time-stamped evidence that removes the guesswork—and the finger-pointing.
The two-way communication features built into many systems also help managers give live feedback or guidance, turning those “uh-oh” moments into teachable ones before they escalate.
It’s not about watching over your drivers—it’s about watching out for them. And when safety becomes collaborative, trust gets stronger across the entire fleet.
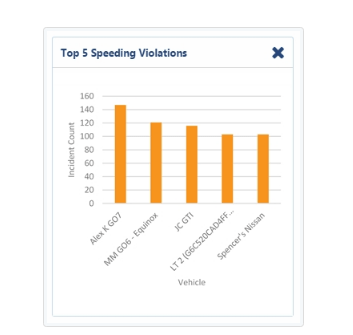
Driver Scorecards: Real-Time Performance Ranking
Once you’ve got visibility, the next step is turning what you see into action. That’s where driver scorecards take the wheel.
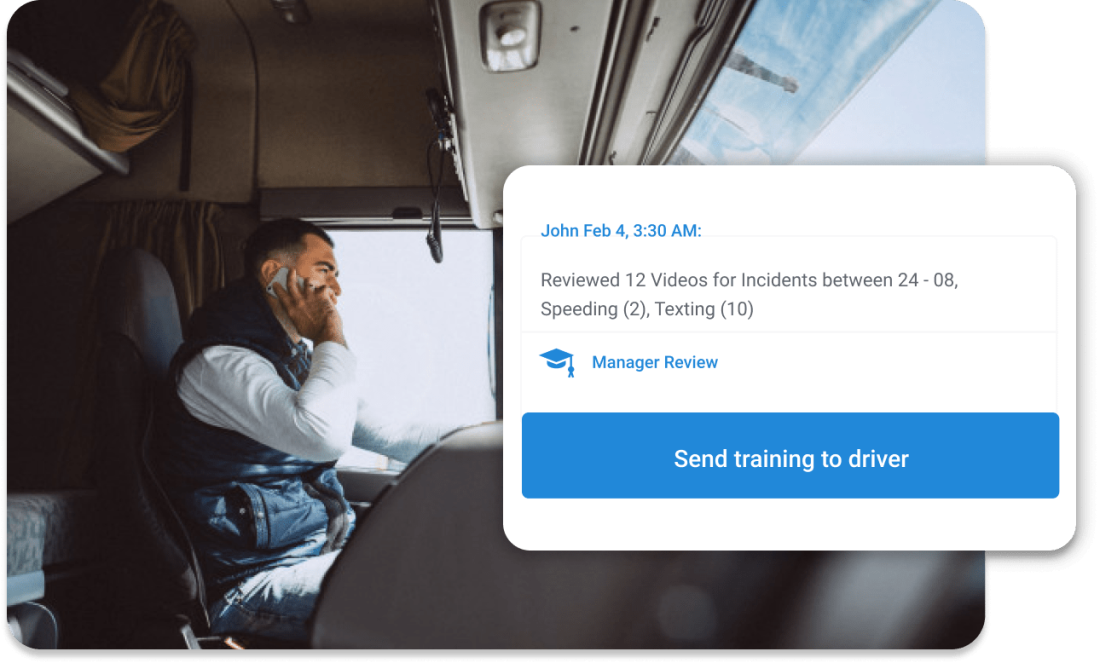
Dash cams help you spot incidents—but scorecards help you track behavior trends, rank performance, and coach with confidence. Instead of relying on reactive reports or gut checks, scorecards translate driver actions into clear, measurable data points.
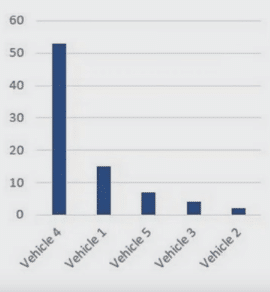
Each driver gets a dynamic performance profile, updated in real time. These systems track metrics like speeding, harsh braking, rapid acceleration, distracted driving, cornering, and even seatbelt use. The result? You can identify your safest drivers, spot those at risk, and tailor coaching with pinpoint accuracy.
You can also segment performance by route type, shift, region, or vehicle class. This way, you’re not just comparing apples to oranges—you’re evaluating drivers based on the unique conditions they face.
The impact goes beyond safety. According to the Virginia Tech Transportation Institute, fleets that adopt scorecard-based coaching programs reduce risky driving behaviors by up to 52% within the first 6 weeks.
When coaching becomes data-driven, drivers are more open to feedback—because it’s fair, consistent, and rooted in facts, not assumptions. That’s how you shift the culture from defensive to accountable.
Gamification: Make Safety Fun and Rewarding
Once drivers understand how they’re being measured, the next challenge is keeping them motivated—and gamification is the secret weapon that makes it happen.
Driver scorecards give you the data.
Gamification gives your team a reason to care about it. Instead of making safety feel like a checklist or a lecture, gamification turns performance improvement into something drivers actually want to participate in.
Leaderboards showcase top performers across safety categories—like smooth braking, zero speeding events, or consistent seatbelt use. Drivers start comparing scores (in a good way), pushing each other to improve. Weekly or monthly challenges like “No Harsh Braking Week” keep engagement high and morale even higher.
The incentives don’t need to be big.
Recognition, digital badges, and small rewards like gift cards or preferred shift assignments go a long way. Drivers who feel acknowledged are more likely to buy into your safety culture and stick around longer.
And it works: According to a study by the National Safety Council, companies that gamify safety programs see up to a 48% reduction in safety incidents and significantly higher employee retention.
Gamification doesn’t replace accountability—it enhances it, creating an environment where drivers feel seen, challenged, and supported.
Real-Time Monitoring = Real-Time Action
Motivation and recognition are powerful—but speed matters just as much. When a risky behavior happens on the road, waiting hours (or even days) to address it can mean missed opportunities, increased liability, or worse.
This is where real-time monitoring shifts the game from reactive to responsive.
While scorecards and gamification drive long-term engagement, real-time tools help you address high-risk moments instantly. Speeding alerts, lane drift detection, sudden stops, and signs of fatigue can all be flagged as they happen—giving drivers a chance to self-correct in the moment.
Fleet managers also benefit from real-time access. Whether it’s viewing live video footage, pinpointing a driver’s exact location, or responding to an emergency with one tap, managers stay informed and ready to act when it matters most.
This speed of response isn’t just helpful—it’s proven to reduce risk. According to a report from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, fleets that use real-time telematics systems see up to a 38% reduction in serious incidents compared to those relying solely on post-trip data.
By catching issues as they unfold, you’re not just managing safety—you’re actively preventing accidents, protecting lives, and strengthening your operation in real time.
Compliance, Culture, and Long-Term Safety
Real-time response is critical—but sustainable success depends on what happens after the alert.
Once you’ve built a system that identifies and corrects unsafe behavior in the moment, the next step is embedding safety into your culture. Because compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about creating a consistent, accountable environment where drivers feel supported and policies stick.
Smart driver management platforms make it easier to formalize that culture. Digital records of HOS logs, ELD compliance, safety events, and coaching sessions give you a structured, defensible history for every driver. That’s a game-changer when it comes to audits, promotions, or disciplinary actions.
It also helps you make better hiring decisions. With access to analytics-backed driver profiles, you can evaluate new applicants on more than just resume claims—you can spot trends in safety history and performance before they join your fleet.
And here’s the long-term payoff: fleets that prioritize safety culture through ongoing training and digital tracking see up to a 42% reduction in preventable collisions, according to the American Transportation Research Institute.
When safety becomes part of how you operate—not just a policy on paper—you get fewer incidents, lower insurance costs, and a team that takes pride in doing things the right way.
What to Look For in a Driver Management System
So, you’ve built the foundation: visibility, coaching, real-time response, and a safety-first culture. But all of that depends on the tools you choose to support it.
The wrong driver management system can leave you stuck with scattered data, poor user experience, and limited ROI. The right system, on the other hand, becomes your central hub for visibility, engagement, and long-term performance improvement.
The best systems do more than just monitor—they empower. They turn raw telematics into usable insights, automate coaching workflows, and make it easy to reward great driving while addressing risk before it becomes a liability.
Here’s what to look for:
- AI Dash Cams with In-Cab Alerts — Real-time audio/visual feedback to prevent incidents as they happen
- Customizable Driver Scorecards — Tailored to your fleet’s specific metrics and goals
- Automated Coaching Triggers — Based on behavior thresholds like hard braking or distractions
- Gamification & Incentive Tools — To keep drivers engaged and motivated
- Real-Time Visibility & Alerts — Across vehicle locations, driver behavior, and route progress
- Mobile-Friendly Driver Interfaces — For easy feedback, communication, and participation
- Integrated Compliance Tools — That sync with ELDs, HOS logs, and audit-ready reports
Choosing the right system isn’t just a tech decision—it’s a strategic one. In fact, according to Frost & Sullivan, fleets using integrated telematics and driver management platforms report 19.5% higher driver retention rates over a 12-month period.
Because when your tools work for your team, your team works better—period.
Unlock Performance with Data-Driven Confidence
The right system isn’t just a tool—it’s a turning point.
Everything we’ve covered leads here: better visibility, real-time response, smarter coaching, stronger culture, and the right technology to hold it all together. But the real value comes when you connect those dots and unlock a fleet that performs at its highest level—consistently.
Because when decisions are backed by real data, coaching becomes fairer, safety becomes proactive, and performance becomes predictable. Your best drivers get the recognition they deserve. Your riskiest drivers get the support they need. And your operations run with more precision, less stress, and fewer surprises.
And the impact is measurable. According to Deloitte, fleets that implement performance-based driver programs powered by telematics see up to a 14% reduction in total operating costs within the first year.
No more guesswork. No more blind spots. Just a smarter, safer, more confident way to lead.
Ready to See It in Action?
Data is powerful—but only when you use it. You’ve now seen how the right tools can transform how you manage, coach, and retain drivers. So the real question is: what are you waiting for?
Your fleet already has the potential. What it needs is visibility. When your decisions are backed by real insights—not guesswork—you make smarter calls, reduce risk, and empower your drivers to succeed.
GoFleet’s driver performance platform is built to help fleets like yours turn real-time data into lasting results. From in-cab AI dash cams to customizable scorecards and proactive coaching workflows, we make it easier to lead with confidence—and prove it on paper.
Let’s put your driver data to work.
Book a demo today and discover how GoFleet can help you unlock the safest, smartest version of your fleet.