Fleet management involves the administration and coordination of vehicles used by companies and organizations to support their operations. This includes managing aspects such as vehicle maintenance, fuel consumption, tracking and diagnostics, driver management, safety compliance, and overall efficiency optimization.
The goal of fleet management is to ensure that the fleet is operationally sound, cost-effective, and adheres to regulations, while also maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of each vehicle.
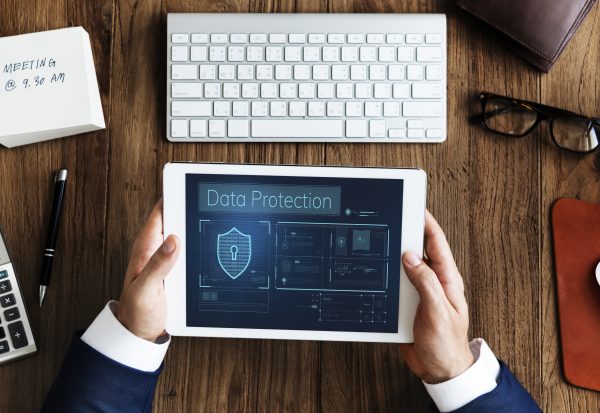
Data security in fleet management is crucial due to the extensive and sensitive nature of the data collected and processed. This data not only includes vehicle and driver information but also encompasses operational details, routes, and logistics, which are vital for the smooth functioning of the fleet.
In 2022, cloud-based fleet management services accounted for 65% of the total market share, highlighting the significant shift towards digital solutions and the increasing importance of safeguarding this data from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and breaches.
In this post, we will delve into the various aspects of data security within the realm of fleet management. We’ll explore the types of data involved, the threats and challenges to data security, and the best practices for ensuring the protection and integrity of this data.
This post will also examine the legal and compliance aspects, the role of technology in enhancing data security, and provide case studies of successful implementations. Lastly, it will look ahead at the future of data security in fleet management, discussing emerging trends and technologies.
Understanding the Data in Fleet Management
Fleet management systems collect a wide array of data critical for efficient operation. This includes vehicle location and routes, fuel consumption, maintenance records, driver behavior and performance metrics, vehicle diagnostics, and compliance data.
Additionally, operational data such as scheduling, dispatch, and delivery details are also integral. Personal data of employees, including contact information and driving records, is often part of the dataset.
The Role of Data in Fleet Operations and Decision Making
Data plays a pivotal role in optimizing fleet operations and strategic decision-making. Real-time location data aids in route planning and improving dispatch efficiency. Fuel consumption and maintenance data help in reducing operational costs and extending vehicle life.
Analysis of driver behavior data can enhance safety and training programs. Overall, this data supports informed decisions, leading to increased efficiency, compliance, and cost savings.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
With the extensive collection of sensitive data, fleet management systems are vulnerable to various risks. Cybersecurity risks include hacking, data breaches, and malware attacks. Physical risks involve the theft or tampering of vehicles and onboard devices.
In addition, internal risks like employee misconduct or inadvertent data leaks due to lack of training pose significant threats. Inadequate data protection measures can lead to financial losses, legal repercussions, and damage to reputation.
Cybersecurity Threats
- Hacking and Unauthorized Access: Fleet management systems, being interconnected and online, are susceptible to hacking. Hackers may gain unauthorized access to sensitive data such as vehicle locations, driver information, and operational details, leading to data breaches and misuse.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malware can infect fleet management systems, disrupting operations and compromising data integrity. Ransomware attacks can lock out users from their systems, demanding payment for data release, severely impacting operations and causing financial losses.
Physical Threats
- Theft of Devices or Vehicles: Theft of vehicles or on-board devices like GPS and data loggers can lead to loss of critical data and hardware. This not only affects operational efficiency but also poses a risk of data being misused or sold.
- Unauthorized Physical Access: Unauthorized access to fleet management devices or vehicles can lead to data tampering or theft, compromising the confidentiality and integrity of the data.
Internal Threats
- Employee Misconduct: Employees with access to fleet management systems can misuse data or intentionally cause harm. This includes data theft, leaking sensitive information, or sabotaging systems.
- Inadequate Training and Awareness: Lack of proper training and awareness among employees about data security practices can lead to inadvertent data breaches, such as through phishing attacks or poor password management. This highlights the need for regular training and reinforcement of data security protocols.
Best Practices for Data Security in Fleet Management
Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Firewalls and Antivirus Software: Implementing firewalls and antivirus software is essential to protect fleet management systems from unauthorized access and malware. These tools act as the first line of defense against external threats.
Regular Software Updates and Patches: Keeping software updated with the latest patches is critical. These updates often include fixes for security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
Data Encryption and Secure Access Controls
Encryption Techniques: Encrypting data ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed unauthorizedly, it remains unreadable and secure.
Access Control Policies: Implementing strict access control policies ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and limiting access based on roles.
Regular Data Backups and Recovery Plans
Having regular data backups is crucial for data security. In the event of data loss due to a cyber-attack, system failure, or other disasters, having an up-to-date backup allows for quick recovery of data.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Regular training and awareness programs for employees are vital. These programs should educate staff about the importance of data security, potential threats, and best practices to follow, such as recognizing phishing attempts and securing their login credentials.
Legal and Compliance Aspects
With the increasing reliance on digital data, understanding and adhering to data protection laws and regulations is crucial for fleet management. According to Gartner, by 2023, 75% of the world’s population will have its personal data covered under modern privacy regulations.
These regulations often dictate how data should be collected, stored, processed, and shared, with a focus on protecting individual privacy and preventing data breaches.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Compliance with industry standards is essential to maintain operational integrity and trust. These standards often encompass data security protocols, operational best practices, and ethical guidelines. Adherence to standards such as ISO 27001, which focuses on information security management, can help fleet management companies ensure that their data handling processes are secure and efficient.
Auditing and Reporting for Compliance
Regular auditing and reporting are important practices to ensure compliance with legal and industry standards. Audits help identify any gaps or weaknesses in data security and compliance measures, allowing for timely rectification. Reporting, on the other hand, ensures transparency and accountability, both internally and to regulatory bodies, regarding the handling and protection of data.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly being used to enhance security in fleet management. These technologies can analyze large volumes of data to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate security threats, such as unusual driver behavior or potential cyberattacks. AI algorithms can provide real-time alerts and automate responses to potential threats, significantly improving the speed and efficiency of security measures.
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to handle data transactions in fleet management. By storing data in a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures that data is tamper-proof and traceable. This technology is particularly useful for maintaining secure records of transactions, vehicle maintenance history, and driver logs, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data.
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone for secure data storage solutions in fleet management. Cloud-based platforms offer scalable and flexible storage options with advanced security measures like encryption, access control, and redundancy. These systems often come with robust backup and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring data availability and protection against data loss. Additionally, cloud service providers typically adhere to strict security protocols and compliance standards, further enhancing data security.
Case Studies: Successful Data Security Implementations in Fleet Management
Below, we analyze companies with robust data security measures. We also outline the lessons learned by these organizations, as well as the best practices that came out of implementation.
Microsoft’s Fleet Management at Global Headquarters:
Microsoft transformed the fleet management at its Redmond headquarters by digitizing transportation and unifying the management of their fleet during the global pandemic. This enabled data-driven decision-making and supported its sustainability goals.
Microsoft implemented a fleet management solution to manage over 500 vehicles, including trucks, passenger vans, and buses. This system enhanced real-time insights and predictive analytics for maintenance, thereby reducing downtime and supporting fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Adapt Integrated Health Care’s Fleet Optimization:
Adapt Integrated Health Care, a nonprofit organization, faced challenges with vehicle tracking and key management using an error-prone Excel spreadsheet. By adopting a fleet management software solution, Adapt significantly improved its fleet operations, regaining control over vehicle management and streamlining processes.
This led to efficient support of their mission, employee growth, and a reduction in the number of vehicles needed for operations. The implementation of this technology was key in revolutionizing their fleet operations and enhancing their ability to provide healthcare services.
Basin Electric Power Cooperative’s Fleet Management Enhancement:
Basin Electric Power Cooperative (BEPC) transformed its fleet management practices to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Initially using manual practices for a fleet of 1,200 units, BEPC implemented fleet management software to automate processes and provide centralized, standardized data.
This change led to a reduction in fleet size by 25 to 30%, saving approximately $100,000 in vehicle acquisition costs and generating annual savings of $20,000. The implementation also curbed inefficient practices and enhanced service levels through data-driven decisions.
City of Stamford’s Cost-Saving Vehicle Sharing System:
The City of Stamford managed a fleet of 1,100 vehicles and faced efficiency issues with its 80 passenger vehicles. Implementing a fleet management solution enabled streamlined operations, including vehicle sharing policies.
This led to a reduced vehicle count and significant cost savings, with ongoing savings of $356,000 within two years and projected 5-year savings exceeding $1 million. The software’s features included online reservations, automated dispatching, and comprehensive data tracking to transform vehicle utilization and optimize fleet operations.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices Derived
- Digital Transformation and Data Utilization: These case studies highlight the importance of digital transformation and the effective utilization of data in fleet management. By adopting advanced software solutions and focusing on data-driven decision-making, organizations can significantly enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service levels.
- Importance of Real-Time Insights and Predictive Analytics: Implementing systems that provide real-time insights and predictive analytics can drastically reduce operational downtimes and support proactive maintenance and sustainability goals.
- Customization and Flexibility in Fleet Management Solutions: The success of these implementations underscores the need for customizable and flexible fleet management solutions that can cater to the specific needs of an organization.
- Employee Engagement and Training: Effective implementation also involves employee engagement and training, ensuring that staff are comfortable and proficient with the new systems.
- Holistic Approach to Fleet Management: A holistic approach that addresses not just vehicle tracking but also key management, reservation systems, and data analytics can lead to comprehensive improvements in fleet management.
The Future of Data Security in Fleet Management
At the outset, the future of data security in fleet management is likely to be shaped by emerging trends and technologies. These include the increased use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time tracking and monitoring, the integration of advanced AI and machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics and threat detection, and the utilization of blockchain for secure, tamper-proof data transactions.
In addition, advancements in biometric security systems and quantum computing are expected to offer new dimensions to data protection.
Predictions for Data Security Challenges and Solutions
With these technological advancements, new data security challenges are likely to emerge. The growing complexity and interconnectedness of systems may lead to increased vulnerabilities and sophisticated cyberattacks. However, solutions are also evolving.
Anticipating these challenges, the industry is expected to focus more on proactive threat detection systems, enhanced encryption technologies, and robust disaster recovery and response strategies.
Furthermore, the emphasis on regulatory compliance and ethical data management will likely intensify, leading to stricter standards and protocols for data security in fleet management.
Final Thoughts
The importance of proactive data security measures can neither be overstated nor undervalued. As technology evolves, so do the challenges and threats to data security. Implementing robust, forward-thinking strategies is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring the smooth operation of fleet management systems.
Keeping up with the latest trends, challenges, and solutions in data security is essential for any fleet management operation. Continuous assessment and improvement of security measures, alongside adherence to legal and compliance standards, are key to safeguarding data.
For more personalized recommendations, contact your GoFleet specialist. Our experts can provide tailored solutions and guidance to enhance the data security of your fleet management operations.