GPS Fleet Monitoring: Pro Concepts
Welcome to Part 2 of our GPS fleet monitoring guide. In our last entry, we caught up with essential GPS fleet monitoring concepts such as Live Map, Rules, Fuel Reports, and Maintenance Reminders.
However, Pro fleet managers go beyond average data skills by learning and using powerful tools. We’ll cover some Pro-level concepts in this guide by reviewing Grouping, Advanced Coaching, Dispatching & Routing, and Engine Diagnostics.
Grouping
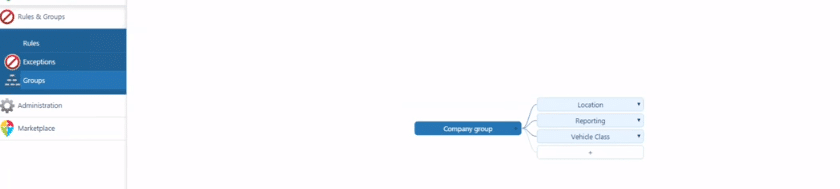
Firstly, Pro fleet managers should know how to group their fleet. Sometimes, a fleet might have multiple divisions and branches. Each branch might have their own manager and their own policies.
Therefore, fleet managers need to learn how to group data. After grouping, fleet managers can create rules for each specific branch and ensure that data is only shared with its respective branch.
For instance, Geotab has a Rules & Groups portal. Fleet managers can manage data by clicking on Groups and adding branches. Then, fleet managers can filter Maps or Exception Reports by created groups.
Advanced Driver Coaching
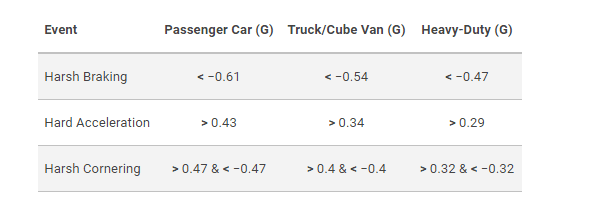
Previously on the Essential GPS Fleet Monitoring blog post, we covered speeding rules. While speeding is absolutely an essential and useful datapoint, Pro fleet managers use other driver coaching metrics. Some of the best driver coaching data include Harsh Braking, Harsh Acceleration, and Harsh Cornering.
Advanced driver coaching is a powerful GPS fleet monitoring tool because managers can give better feedback to drivers and improve fleet objectives. For instance, studies indicate that harsh acceleration is closely linked to fuel usage and distracted driving. Fleets that monitor and control harsh acceleration significantly improve fuel and safety scores.
Geotab monitors acceleration and braking events through G-shock detectors. Furthermore, managers can control acceleration events by playing with their sensitivity. Some of the recommended G-shock settings include:
Dispatching & routing
Another Pro concept is dispatching and routing drivers. Pro fleet managers minimize fuel expense and simplify operations through effective route planning.
Typically, this involves plotting job sites on a map, sending jobs to drivers, and then monitoring route compliance. To illustrate, we’ll show these three functions on the Geotab platform.
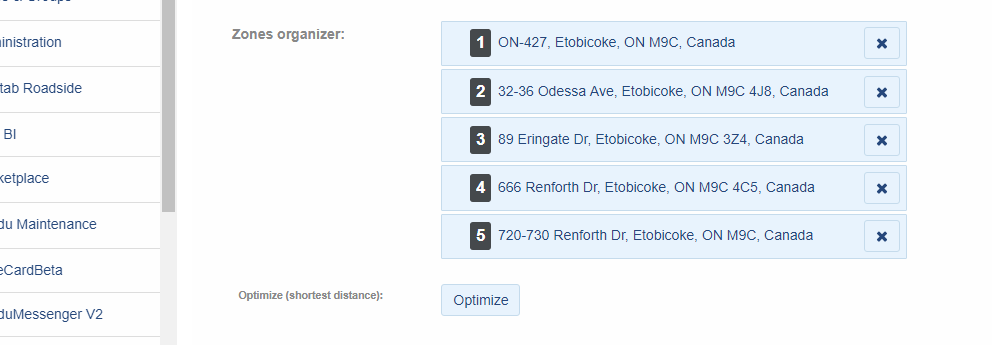
Scheduling Routes
Firstly, fleet managers need to create routes. Fleet managers usually draw routes, import routes from a database, or use route optimization software. Geotab users can go into Zones & Messages and click Routes to create a route.
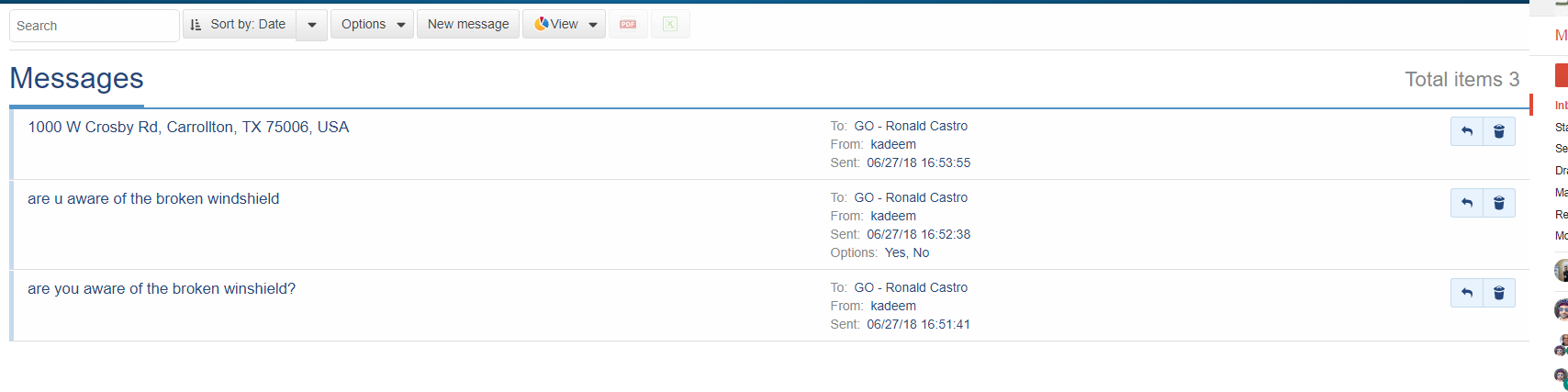
Sending Jobs to Drivers
Secondly, after scheduling routes, fleet managers communicate with their team. Managers can click “Send Route to Vehicle” on the Routes page to send route to a driver’s Geotab Drive app. Also, managers can access the Message portal to chat with their drivers.
Monitoring Route Compliance
Finally, managers can monitor route compliance and productivity through reports. Two of the most popular reports include “Unmatched Routes” and “Planned vs. Actual Routes”. Unmatched Routes indicate when drivers stop at unassigned destinations, whereas Planned vs. Actual Routes show when drivers deviate from set plans.
Engine Diagnostics Data
Lastly, we’ll cover Engine Diagnostics Data, which is another Pro fleet management skill. While Maintenance Reminder is a good essential concept, Engine Diagnostics Data allow fleet managers to check engine codes and plan preventative maintenance.
Why is that so powerful? Normally, fleet managers have to take their vehicles to a shop to read engine data. However, because telematics devices remotely reads engine codes, fleet managers can pull engine data from their desk. Managers can then decide when to take the vehicle to the shop based on fault severity.
Engine Measurements
Also, managers can check a vehicle’s health by data such as battery voltage, cranking voltage, and engine RPM.
Click here to schedule Pro Training on Best Practices & Reports.